Postgresql Container

- Step1 pull image https://hub.docker.com/_/postgres/
$ docker pull postgres
- Step2 Run container
$ docker run --name my-postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=my_password -d -p 5432:5432 postgres
$ docker ps
-
Explaination
- my-postgres is the name of the container (you can choose a different name if you prefer).
- my_password is the password you want to set for the “postgres” user in PostgreSQL.
- The -d option runs the container in the background.
- The -p 5432:5432 option maps port 5432 from the container to port 5432 on the host, allowing you to connect to PostgreSQL from the host.
-
Step3 check port
$ docker port my-postgres
5432/tcp -> 0.0.0.0:5432
- Step4 Access point
pull image postgres addmin
- Step 5 Run
docker run --name test-pgadmin -p 15432:80 -e "PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL=my_email@test.com" -e "PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD=my_password" -d dpage/pgadmin4
-
Explaination
- test-pgadmin is the name of the container being created.
- The -p 15432:80 option maps port 15432, which is used for communication with pgAdmin, to port 80.
- PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL will be the login you use to access pgAdmin.
- PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD will be the password you use to access pgAdmin.
-
prepare firewall-cmd
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5432/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
access to dashboard
http://192.168.33.10:15432/
After logging in with the defined email (my_email@test.com) and password (my_password), the main panel will appear
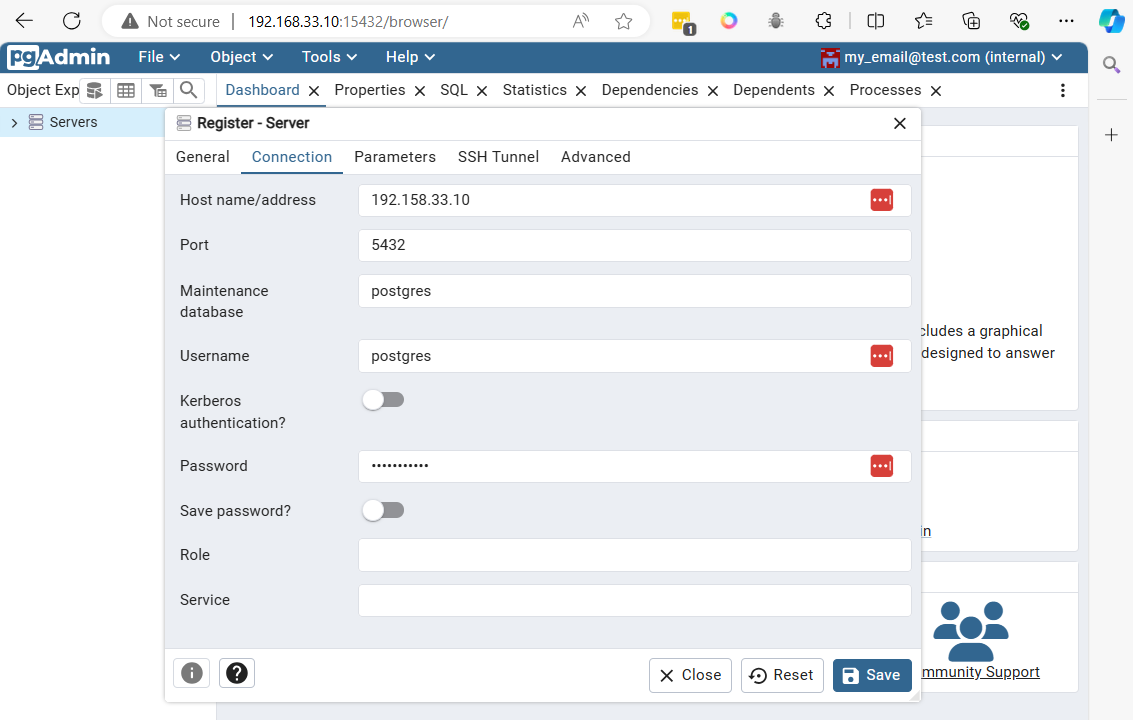
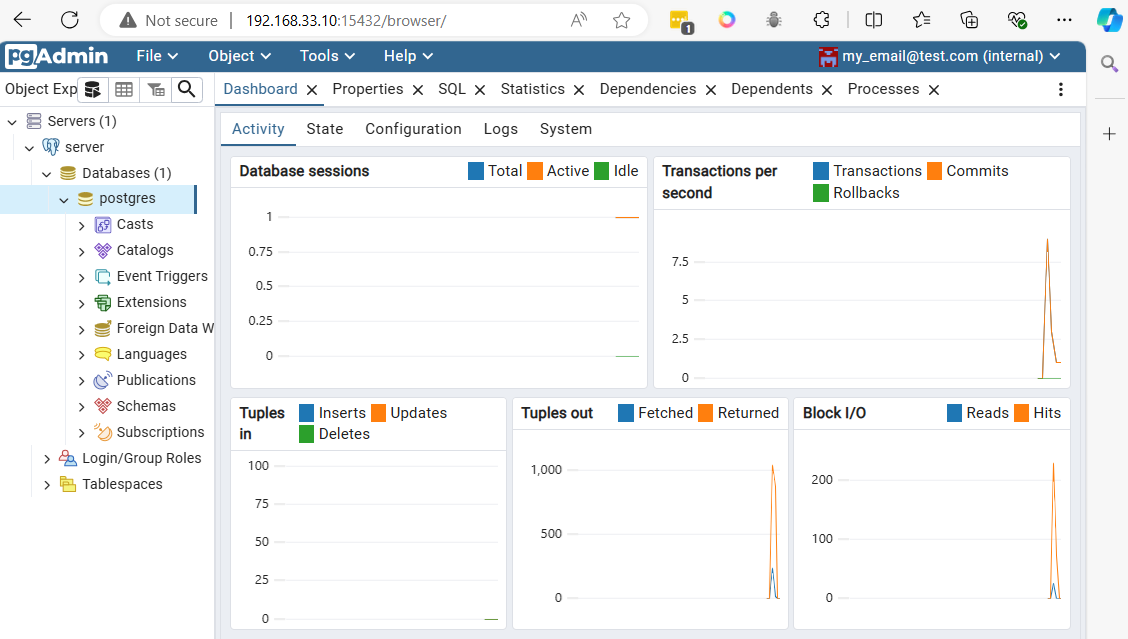
Connect to postgresql from vagrant command line
sudo ss -tulpn | grep 5432
sudo dnf install postgresql
connnect with command line
PGPASSWORD=my_password psql -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres
// result
psql (13.16, server 16.4 (Debian 16.4-1.pgdg120+1))
WARNING: psql major version 13, server major version 16.
Some psql features might not work.
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# \q
$ PGPASSWORD=my_password psql -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres -c '\l'
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+------------+------------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.utf8 | en_US.utf8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.utf8 | en_US.utf8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.utf8 | en_US.utf8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(3 rows)
- Clean all
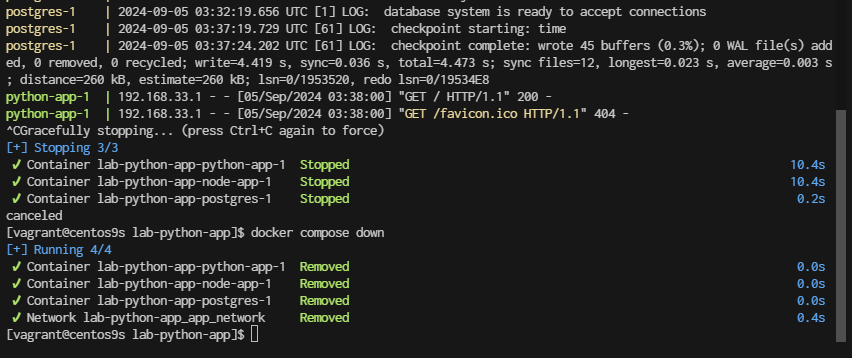
$ docker stop $(docker ps -q)
$ docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
Create Dockerfile
$ mkdir postgresq
$ cd postgres
$ cat <<EOF | tee docker-compose.yml
services:
postgres:
image: postgres
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: my_password
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
- pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- pg_network
pgadmin:
image: dpage/pgadmin4
environment:
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL: my_email@test.com
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD: my_password
ports:
- "15432:80"
networks:
- pg_network
networks:
pg_network:
volumes:
pgdata:
EOF
$ cat docker-compose.yml
- Docker compose
$ docker compose up -d
[+] Running 4/4
✔ Network postgres_default Created 0.5s
✔ Volume "postgres_pgdata" Created 0.0s
✔ Container postgres-postgres-1 Started 0.5s
✔ Container postgres-pgadmin-1 Started 0.5s
- Clean
$ docker stop $(docker ps -q)
$ docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
Containerize Application
Application structure
.
├── docker-compose.yml
├── node-app
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ ├── app.js
│ ├── package.json
└── python-app
├── Dockerfile
└── app.py
create application
cd ~
mkdir lab-python-app
cd lab-python-app
mkdir {node-app,python-app}
-copy paste code below to terminal: create file: docker-compose.yml
cat <<EOF | tee docker-compose.yml
services:
postgres:
image: postgres
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: my_user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: my_password
POSTGRES_DB: my_database
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
- pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- app_network
node-app:
build: ./node-app
environment:
DB_HOST: postgres
DB_USER: my_user
DB_PASSWORD: my_password
DB_NAME: my_database
depends_on:
- postgres
ports:
- "3000:3000"
networks:
- app_network
python-app:
build: ./python-app
environment:
DB_HOST: postgres
DB_USER: my_user
DB_PASSWORD: my_password
DB_NAME: my_database
depends_on:
- postgres
ports:
- "5000:5000"
networks:
- app_network
networks:
app_network:
volumes:
pgdata:
EOF
-copy paste code below to terminal: create file: node-app/Dockerfile
cat <<EOF | tee node-app/Dockerfile
FROM node:22
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY . .
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "app.js"]
EOF
-copy paste code below to terminal: create file: node-app/app.js
cat <<EOF | tee node-app/app.js
const { Client } = require('pg');
const client = new Client({
host: process.env.DB_HOST,
user: process.env.DB_USER,
password: process.env.DB_PASSWORD,
database: process.env.DB_NAME,
});
client.connect()
.then(() => console.log('Connected to PostgreSQL from Node.js!'))
.catch(err => console.error('Connection error', err.stack));
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello from Node.js and PostgreSQL!');
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Node.js app listening at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
EOF
-copy paste code below to terminal: create file: node-app/package.json
cat <<EOF | tee node-app/package.json
{
"name": "node-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "A simple Node.js app with PostgreSQL",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "node app.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.17.1",
"pg": "^8.7.1"
}
}
EOF
-copy paste code below to terminal: create file: python-app/Dockerfile
cat <<EOF | tee python-app/Dockerfile
FROM python:3.12
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
COPY requirements.txt ./
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
EXPOSE 5000
CMD ["python", "./app.py"]
EOF
-copy paste code below to terminal: create file: python-app/requirements.txt
cat <<EOF | tee python-app/requirements.txt
flask
psycopg2
EOF
-copy paste code below to terminal: create file: python-app/app.py
cat <<EOF | tee python-app/app.py
from flask import Flask
import psycopg2
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
def connect_db():
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host=os.getenv("DB_HOST"),
database=os.getenv("DB_NAME"),
user=os.getenv("DB_USER"),
password=os.getenv("DB_PASSWORD")
)
return conn
@app.route('/')
def hello():
try:
conn = connect_db()
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT version()')
db_version = cursor.fetchone()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return f"Hello from Python and PostgreSQL! DB version: {db_version}"
except Exception as e:
return str(e)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
EOF
Steps to Run: Build and run the services:
docker compose up --build
Command Usage:
-
docker-compose up --build: This command builds the images and starts the containers. It’s useful when you’ve made changes to your Dockerfiles or the application code, and you need to rebuild the images.
-
docker-compose up -d: This command starts the containers in detached mode (background) using the existing images. If you have made changes and want to ensure the latest images are used, you should run docker-compose up --build first. After the initial build, subsequent runs with docker-compose up -d will use the existing images unless the Dockerfile or docker-compose.yml file changes.
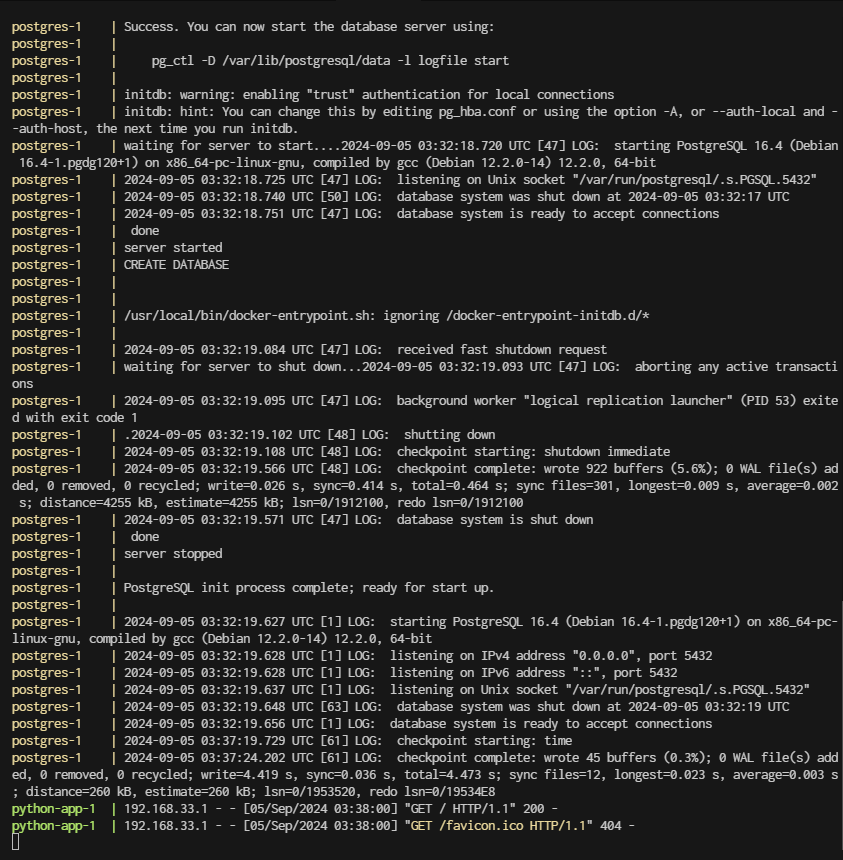
Access the applications:
Node.js app will be running at http://localhost:3000
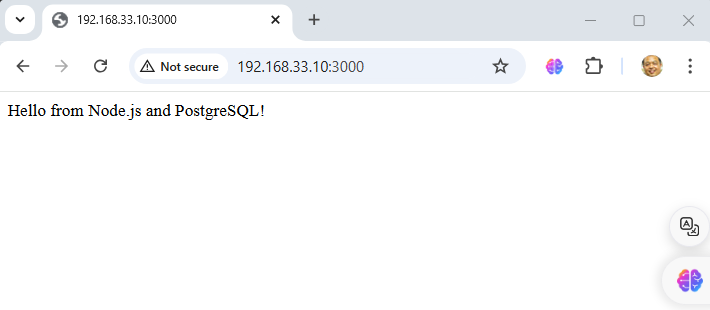 Python app will be running at http://localhost:5000
Python app will be running at http://localhost:5000
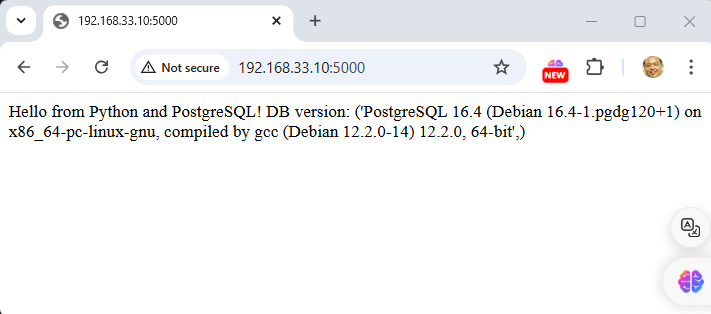
Both applications will connect to the PostgreSQL database using the same credentials.
- Stop application go back to console
- control + c to stop
- run
docker compose down