Basic Deployment with NodePort

Beginners A basic Kubernetes lab setup for beginners to understand how to deploy, scale, and manage applications in a Kubernetes cluster. In this example, we'll deploy an Nginx web server.
Step 1. Prerequisites Ensure you have the following:
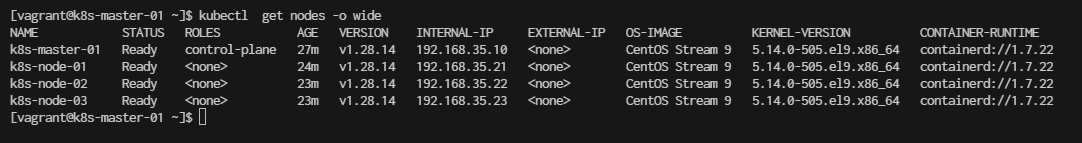
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
k8s-master-01 NotReady control-plane 28m v1.28.13 192.168.35.10 <none> CentOS Stream 9 5.14.0-503.el9.x86_64 containerd://1.7.21
k8s-node-01 Ready <none> 9m59s v1.28.13 192.168.35.21 <none> CentOS Stream 9 5.14.0-503.el9.x86_64 containerd://1.7.21
k8s-node-02 Ready <none> 8m16s v1.28.13 192.168.35.22 <none> CentOS Stream 9 5.14.0-503.el9.x86_64 containerd://1.7.21
k8s-node-03 Ready <none> 7m36s v1.28.13 192.168.35.23 <none> CentOS Stream 9 5.14.0-503.el9.x86_64 containerd://1.7.21
Result output:
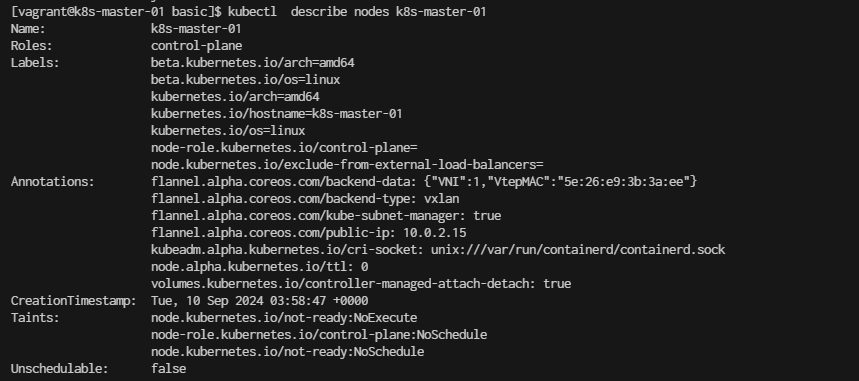
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl describe nodes k8s-master-01
Start workshop 5: Basic Deployment
Step 1. Prepare folder
cd ~
mkdir basic
cd basic
Step 2. Create a Namespace
Namespaces are used to logically separate resources within a Kubernetes cluster. kubectl create namespace my-lab
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 ~]$ kubectl create namespace my-lab
namespace/my-lab created
Step 3. Deploy an Nginx Application We'll create a deployment resource for Nginx, which is a simple web server.
- 3.1 Create a Deployment YAML File Create a file called nginx-deployment.yaml:
cat << EOF | tee nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
namespace: my-lab
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOF
- 3.2 Apply the Deployment
Run the following command to create the Nginx deployment:
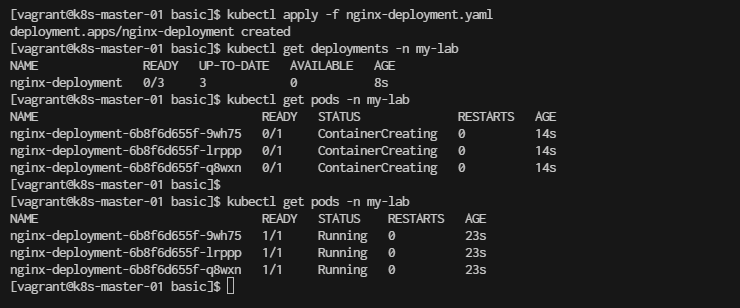
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment created
Verify
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get deployments -n my-lab
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get pods -n my-lab
wait until STATUS is Running
Step 4. Next We Expose the Nginx Application Create a Service to expose the Nginx application.
- 4.1 Create a Service YAML File Create a file called nginx-service.yaml:
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
namespace: my-lab
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: NodePort
EOF
- 4.2 Apply the Service
Run the following command to create the service:
kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yaml
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yaml
service/nginx-service created
Check the service: kubectl get services -n my-lab
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get services -n my-lab
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get services -n my-lab -o wide
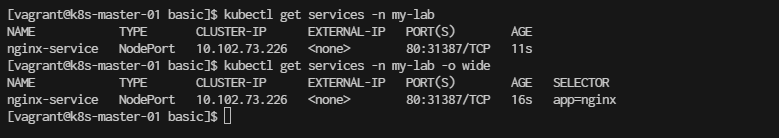
- 4.3 Access the Nginx Application Find the NodePort assigned to your service:
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get svc nginx-service -n my-lab
- From file
nginx-service.yamlport will random select. We will fix nodeport
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl delete -f nginx-service.yaml
create nginx-service-nodeport.yaml fix nodeport 30001
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-service-nodeport.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-nodeport
namespace: my-lab
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: nginx # Same selector as in the LoadBalancer service
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80 # Service Port
targetPort: 80 # Container Port in the nginx pod
nodePort: 30001 # NodePort for external access
EOF
- apply service
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl apply -f nginx-service-nodeport.yaml

- verify
kubectl get svc
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get svc nginx-nodeport -n my-lab
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get svc nginx-nodeport -n my-lab -o wide
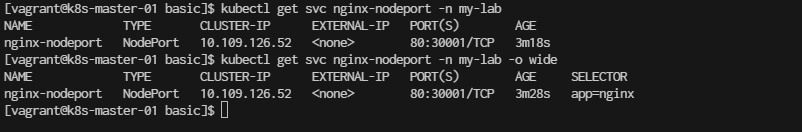
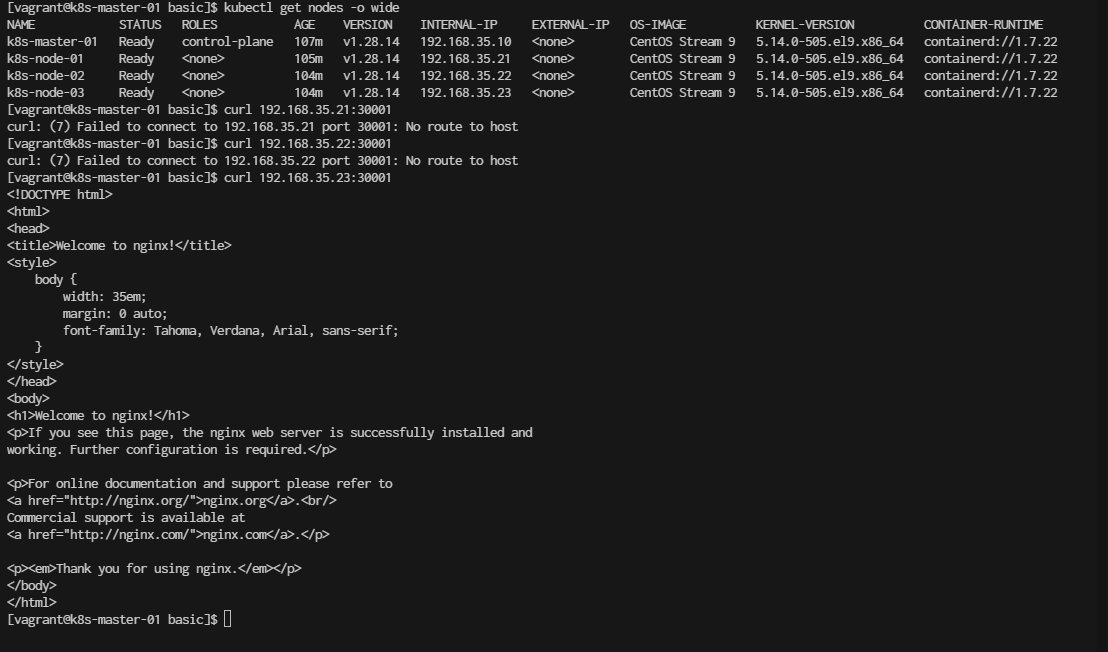
You can now access Nginx using your node’s IP and the assigned port:
http://<node-ip>:<node-port>
(try to connect to every node ip)
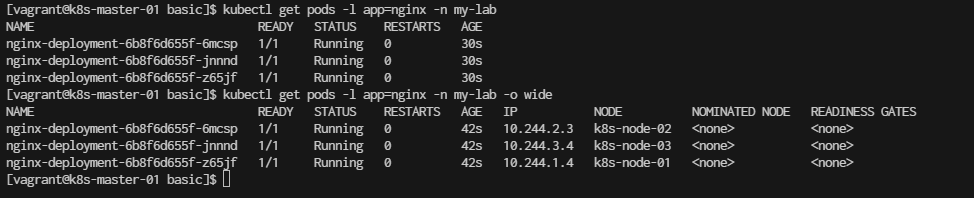
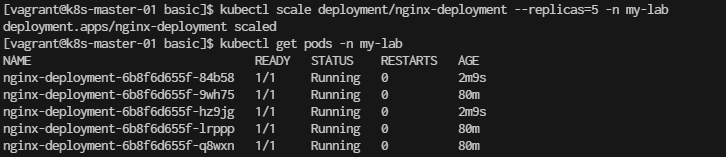
Step 5. Scale the Nginx Deployment You can scale the deployment to run more replicas of Nginx:
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl scale deployment/nginx-deployment --replicas=5 -n my-lab
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment scaled
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl get pods -n my-lab
Result Output:
Step 6. View Nginx Logs
Check the logs of a specific Nginx pod: kubectl logs <nginx-pod-name> -n my-lab
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl logs nginx-deployment-6b8f6d655f-84b58 -n my-lab
Step 7. Clean up, Delete All Resources Once you're done with the lab, you can delete the resources:
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl delete deployment nginx-deployment -n my-lab
deployment.apps "nginx-deployment" deleted
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl delete service nginx-nodeport -n my-lab
service "nginx-nodeport" deleted
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 basic]$ kubectl delete namespace my-lab
namespace "my-lab" deleted
:)