ClusterIP Network
Nginx with a ClusterIP Service
cd ~
mkdir clusterip
cd clusterip
1. create nginx-deployment.yaml
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx # This selector ensures the services will target these pods
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx # Label that matches the selector in services
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOF
Explanation:
- apiVersion: apps/v1 is the current version used for deployments.
- kind: Defines that this resource is a Deployment.
- metadata: The deployment name is nginx-deployment.
- replicas: Specifies that 2 replicas (pods) of Nginx will be created.
- selector: -matchLabels: app: nginx ensures that the pods managed by this deployment are targeted by services with the same selector.
- template:
- metadata: The label app: nginx is applied to the pods created by the deployment. This is critical because services use this label to route traffic to these pods.
- containers: Defines the container inside the pod, in this case, using the nginx:latest image, and exposing port 80 (the default Nginx port).
Deploy the Nginx Deployment
To apply this deployment, run the following command:
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 clusterip]$ kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
verify by kubectl get deployments.apps
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 clusterip]$ kubectl get deployments.apps
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-deployment 0/2 2 0 9s
This deployment ensures that the Nginx pods will be accessible via the NodePort, LoadBalancer, or ClusterIP services you've set up, as all of them have the same selector: app: nginx.
2. Create a ClusterIP Service for Nginx
- create file
nginx-service-clusterip.yaml
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-service-clusterip.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-clusterip
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80 # Service port
targetPort: 80 # Port inside the Nginx pod
EOF
Explanation:
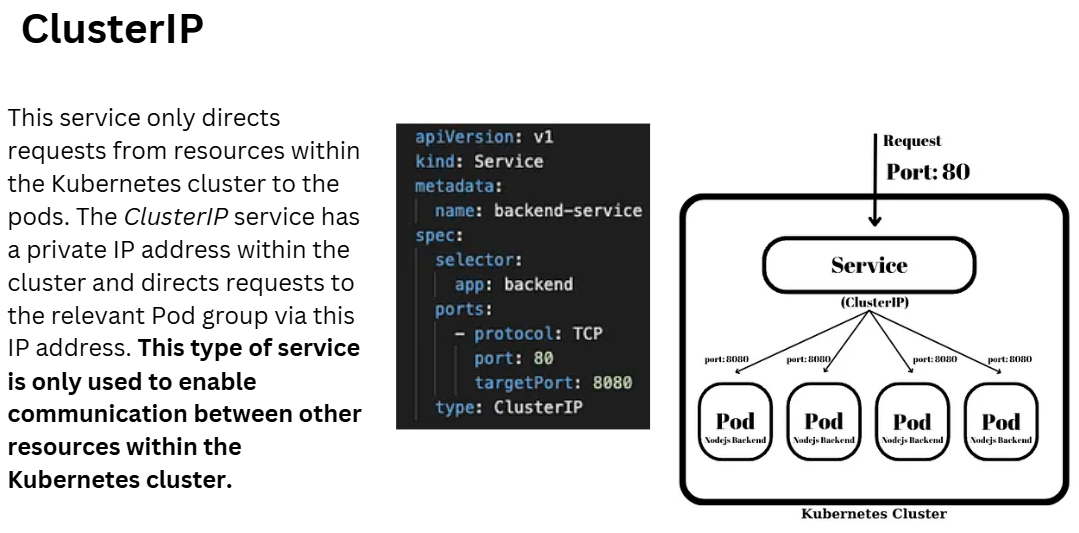
- Type: ClusterIP — This exposes the service on an internal IP in the cluster, only accessible from other services or pods within the cluster.
- The selector (app: nginx) ensures that traffic is routed to the Nginx pods.
Apply the clusterIP service
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 clusterip]$ kubectl apply -f nginx-service-clusterip.yaml
Check the service
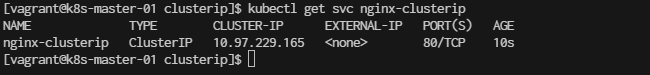
Once the ClusterIP service is created, you can check the details of the service, including the cluster-internal IP address:
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 clusterip]$ kubectl get svc nginx-clusterip
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-clusterip ClusterIP 10.97.229.165 <none> 80/TCP 10s
Result output:
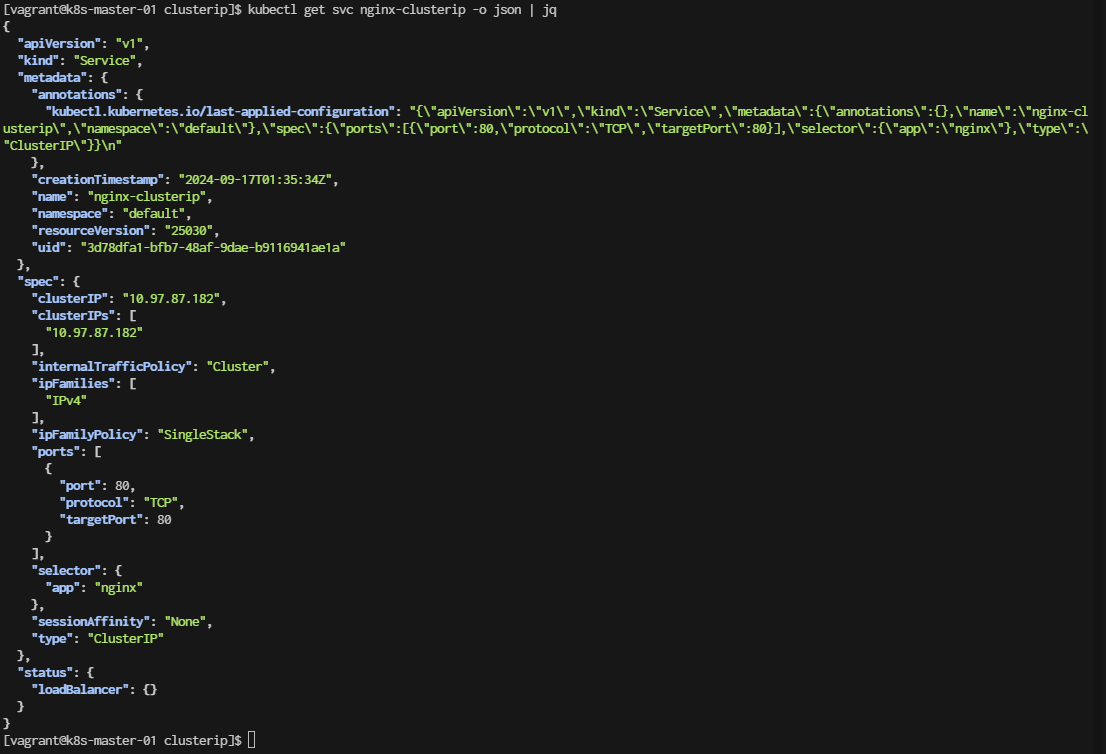
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 clusterip]$ kubectl get svc nginx-clusterip -o json | jq
Check pods logs
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 clusterip]$ kubectl logs -l app=nginx
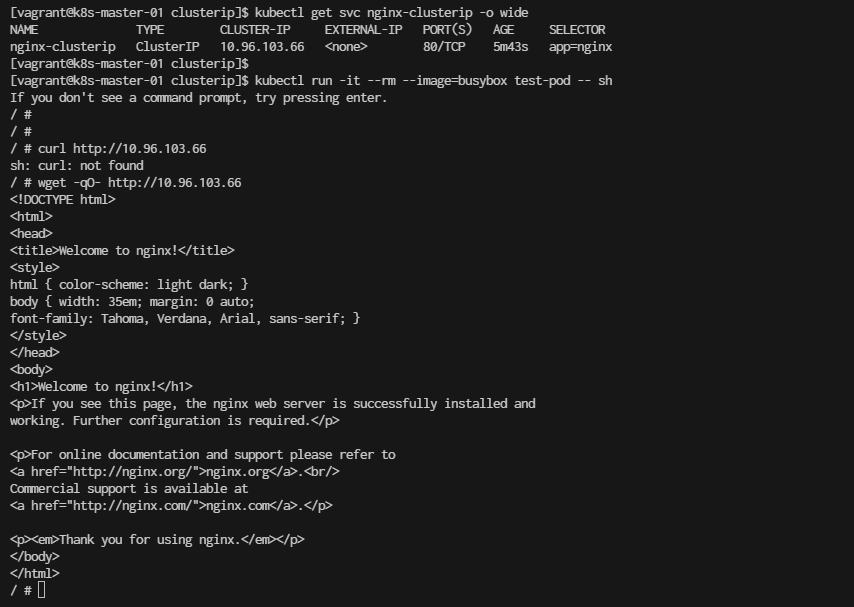
Test ClusterIP Since this is a ClusterIP service, it’s accessible only within the cluster. You can test access to it by running a temporary pod or using another service in the cluster that can reach it.
To test the service, you can run a temporary pod like this:
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 clusterip]$ kubectl run -it --rm --image=busybox test-pod -- sh
Once inside the pod, you can use wget or curl to access the service:
# wget -qO- http://10.96.103.66