MetalLB
Why?
Kubernetes does not offer an implementation of network load balancers (Services of type LoadBalancer) for bare-metal clusters. The implementations of network load balancers that Kubernetes does ship with are all glue code that calls out to various IaaS platforms (GCP, AWS, Azure…). If you’re not running on a supported IaaS platform (GCP, AWS, Azure…), LoadBalancers will remain in the “pending” state indefinitely when created.
Bare-metal cluster operators are left with two lesser tools to bring user traffic into their clusters, “NodePort” and “externalIPs” services. Both of these options have significant downsides for production use, which makes bare-metal clusters second-class citizens in the Kubernetes ecosystem.
MetalLB aims to redress this imbalance by offering a network load balancer implementation that integrates with standard network equipment, so that external services on bare-metal clusters also “just work” as much as possible.
we simulate a LoadBalancer using MetalLB https://metallb.universe.tf/

Allow firewall: run on everynode
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=7946/tcp --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=7472/tcp --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-icmp-block-inversion
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=dhcp --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
$ sudo firewall-cmd --list-ports
- Speaker: Port 7946 (TCP) for communication and service management.
- Controller: Port 8080 (TCP) for managing IP allocation.
Preparation
kubectl get configmap kube-proxy -n kube-system -o yaml | \
sed -e "s/strictARP: false/strictARP: true/" | \
kubectl apply -f - -n kube-system
Installation Metallb by manifest
To install MetalLB, apply the manifest:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.14.8/config/manifests/metallb-native.yaml
https://github.com/metallb/metallb/
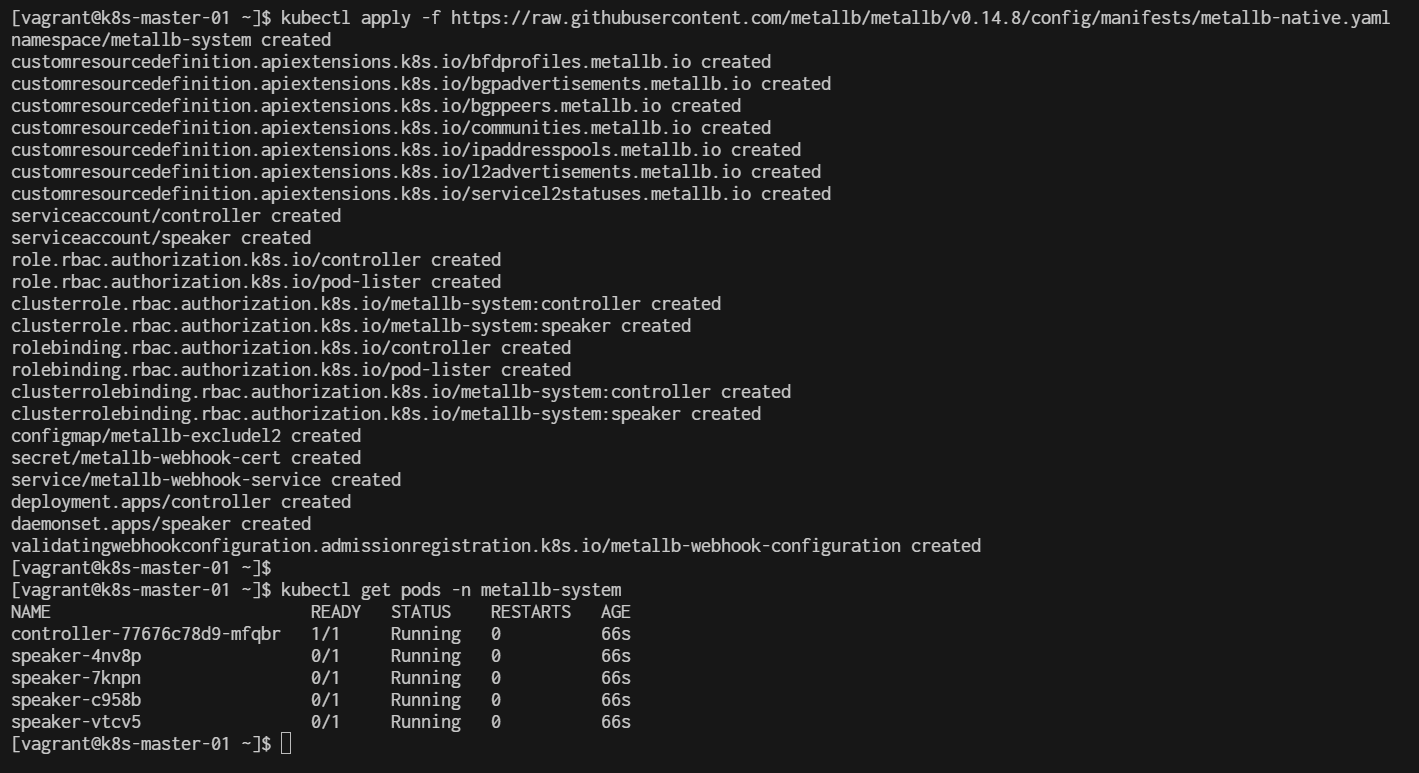
In the context of Kubernetes, a manifest is a YAML or JSON file that defines the desired state of a resource in the cluster. It describes the configuration and specifications of various Kubernetes objects, such as Pods, Services, Deployments, ConfigMaps, and more.
This command will create the necessary components for MetalLB, including the controller and speaker deployments.
Verify the Installation:
$ kubectl get pods -n metallb-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
controller-77676c78d9-wzwwm 1/1 Running 0 39m
speaker-7q7kw 1/1 Running 0 39m
speaker-7t6hm 1/1 Running 0 39m
speaker-gccwq 1/1 Running 0 39m
speaker-wbwrh 1/1 Running 0 39m
- 4 node will have 4
speaker-<speake-pod-name>
$ kubectl logs -n metallb-system <controller-pod-name>
$ kubectl logs -n metallb-system <speake-pod-name>
example:
kubectl logs -n metallb-system controller-77676c78d9-wzwwm
kubectl logs -n metallb-system speaker-7q7kw
show pods and log:
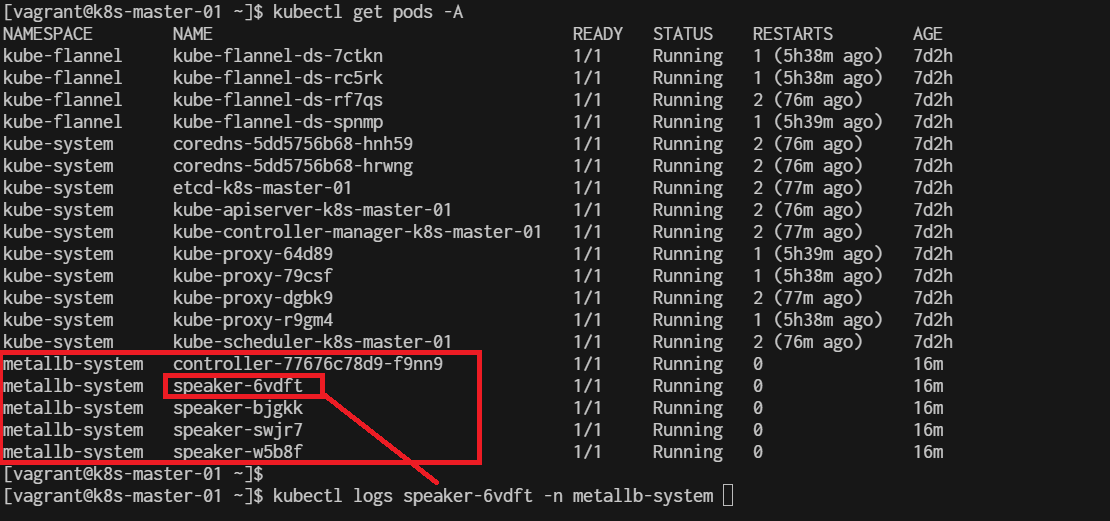
get event
$ kubectl get events -n metallb-system
Describe pod:
$ kubectl describe pods -n metallb-system
Configure MatalLB
MetalLB needs a configuration to know which IP addresses it can use. You can create a ConfigMap to specify a pool of IP addresses. Here’s an example:
Create a file named metallb-config.yaml with the following content:
cat <<EOF | tee metallb-config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: metallb-system
name: config
data:
config: |
address-pools:
- name: default
protocol: layer2
addresses:
- 192.168.1.200-192.168.1.210
EOF
apply configmap
$ kubectl apply -f metallb-config.yaml
$ kubectl get pods -A
verify config map
$ kubectl get configmap config -n metallb-system -o yaml
descripe
$ kubectl describe configmap config -n metallb-system
output to yml:
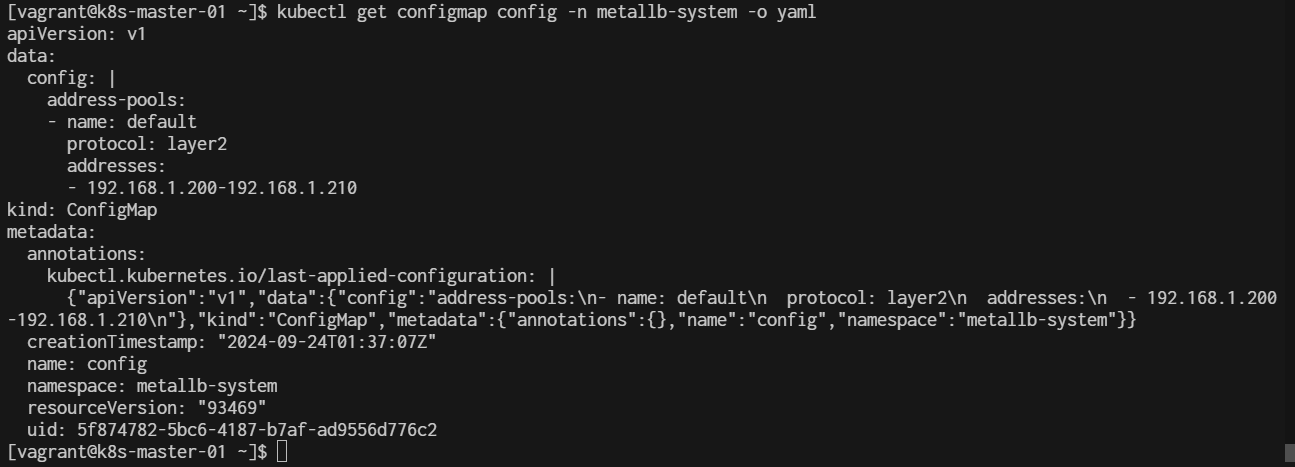
- if needed to delete please run command delete
kubectl delete configmaps config -n metallb-system
show how to log event:
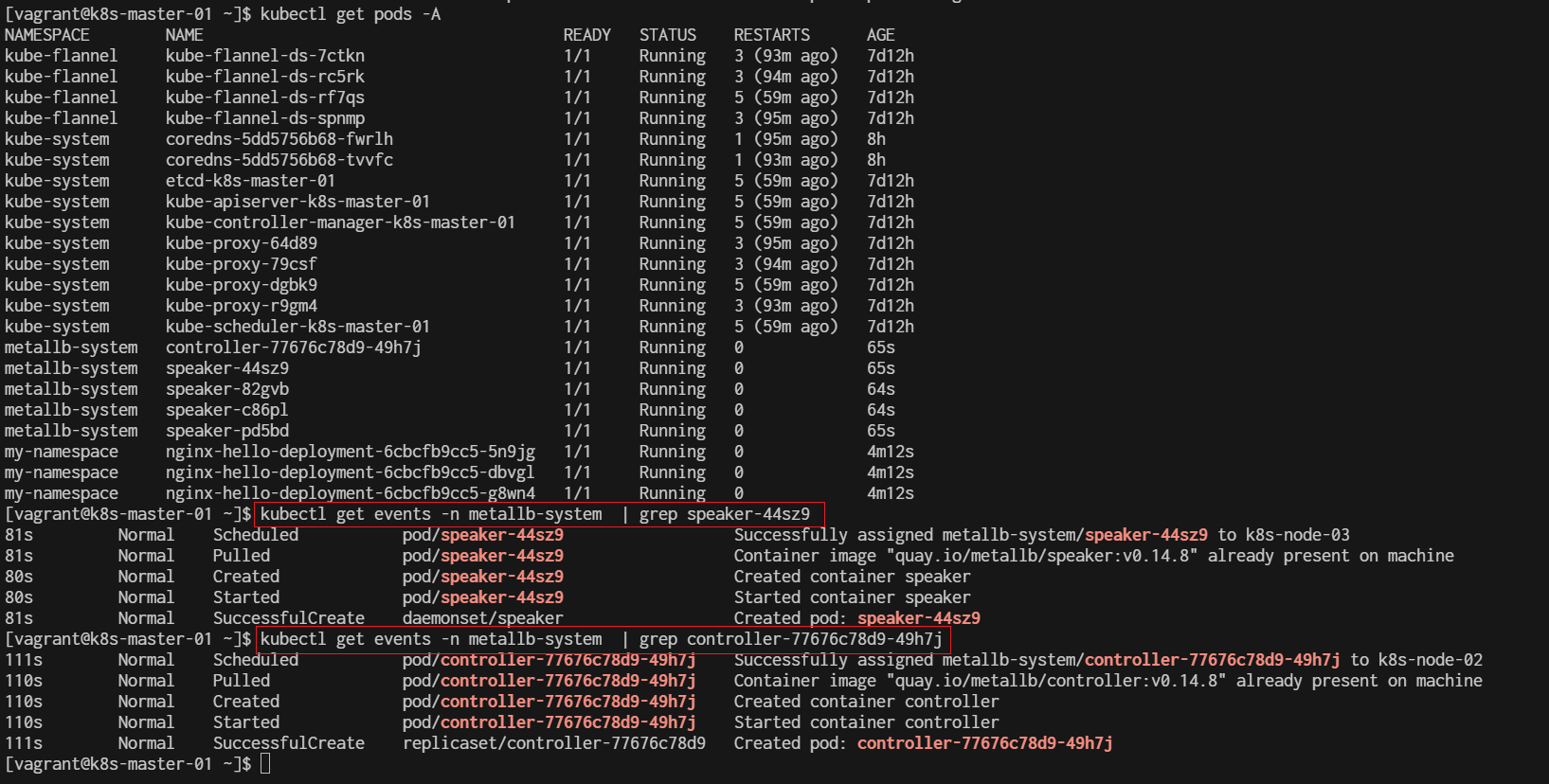
Create Deployment
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-hello-deployment
namespace: my-namespace # Replace with your namespace if necessary
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-hello
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-hello
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-hello
image: nginxdemos/nginx-hello:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-hello-service
namespace: my-namespace # Replace with your namespace if necessary
spec:
selector:
app: nginx-hello
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer
EOF
Apply menifest:
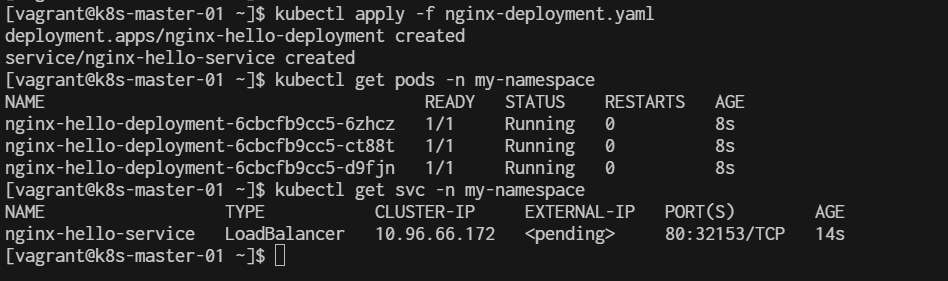
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
$ kubectl get pods -A
$ kubectl get pods -n my-namespace
$ kubectl get svc -n my-namespace
External IPs:
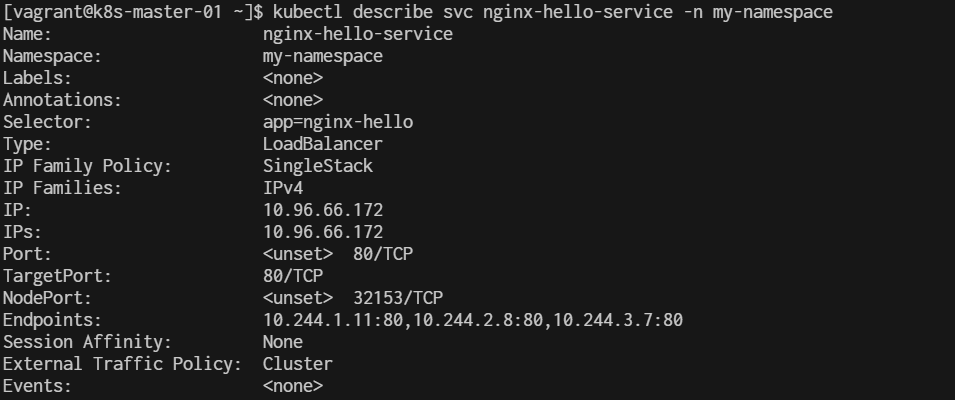
The kubectl describe svc and kubectl get svc commands will display the external IP of a Service.
$ kubectl describe svc nginx-hello-service -n my-namespace
Summary kube command
kubectl get nodes -o wide
kubectl get all --all-namespaces
kubectl get all # namespace defalut
kubectl get all -n metallb-system # namespace metallb-system
kubectl describe configmap config -n metallb-system # configmap
kubectl describe configmap -n kube-system kube-proxy
kubectl describe pods -n metallb-system
Delete
$ kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.14.8/config/manifests/metallb-native.yaml
$ kubectl delete -f nginx-deployment.yaml && kubectl delete -f metallb-config.yaml
Delete resource
$ kubectl get deployments -A
$ kubectl delete deployments nginx-hello-deployment -n my-namespace
$ kubectl delete pod -n metallb-system --all
$ kubectl delete services -n my-namespace --all
Restart Metallb component
$ kubectl rollout restart daemonset speaker -n metallb-system
$ kubectl rollout restart deployment controller -n metallb-system
Check Metallb log
$ kubectl logs -n metallb-system daemonset/speaker
$ kubectl logs -n metallb-system deployment/controller
cat <<EOF | tee ipaddresspool.yaml
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: IPAddressPool
metadata:
name: ip-pool
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
addresses:
- 192.168.1.100-192.168.1.120
EOF