Config Kubernetes Network Nginx
- Step 1: Create a Deployment for Nginx First, create a Kubernetes deployment to manage the Nginx pods.
cd ~
mkdir kubernetest_network
cd kubernetest_network
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOF
- Deploy Nginx Pod
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
- Step 2: Expose the Deployment as a Service
2.1 Expose Using NodePort Now, expose the Nginx deployment using a NodePort service, which makes the service accessible on a port of each node in the cluster.
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-service-nodeport.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-nodeport
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: nginx # Same selector as in the LoadBalancer service
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80 # Service Port
targetPort: 80 # Container Port in the nginx pod
nodePort: 30001 # NodePort for external access, specify a NodePort in the range 30000-32767
EOF
Apply nodeport
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-service-nodeport.yaml
2.2 get the Node IP of the nodes in your Kubernetes cluster, you can use the following methods:
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide
2.3 Expose pod and enable external access by using LoadBalance
cat <<EOF | tee nginx-service-loadbalancer.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-loadbalancer
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: nginx # This must match the selector used in nginx-nodeport.yaml
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80 # Service Port
targetPort: 80 # Container Port in the nginx pod
EOF
Explanation:
- Both the NodePort and LoadBalancer services target the same pods (those with the label app: nginx).
- The selector (app: nginx) is common in both services and matches the labels defined in the nginx-deployment pods.
Next we Apply loadbalance
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-service-loadbalancer.yaml
Check the external IP assigned to the LoadBalancer:
$ kubectl get svc nginx-loadbalancer
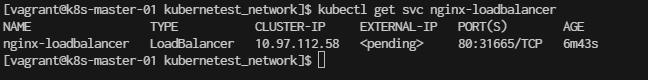
You should see the service with TYPE: LoadBalancer and its CLUSTER-IP (in this case, 10.97.112.58).
Check Service endpoint (pod) is running
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-7c79c4bf97-jphp8 1/1 Running 0 9m42s
nginx-deployment-7c79c4bf97-mn6hw 1/1 Running 0 9m42s
Summary Command:
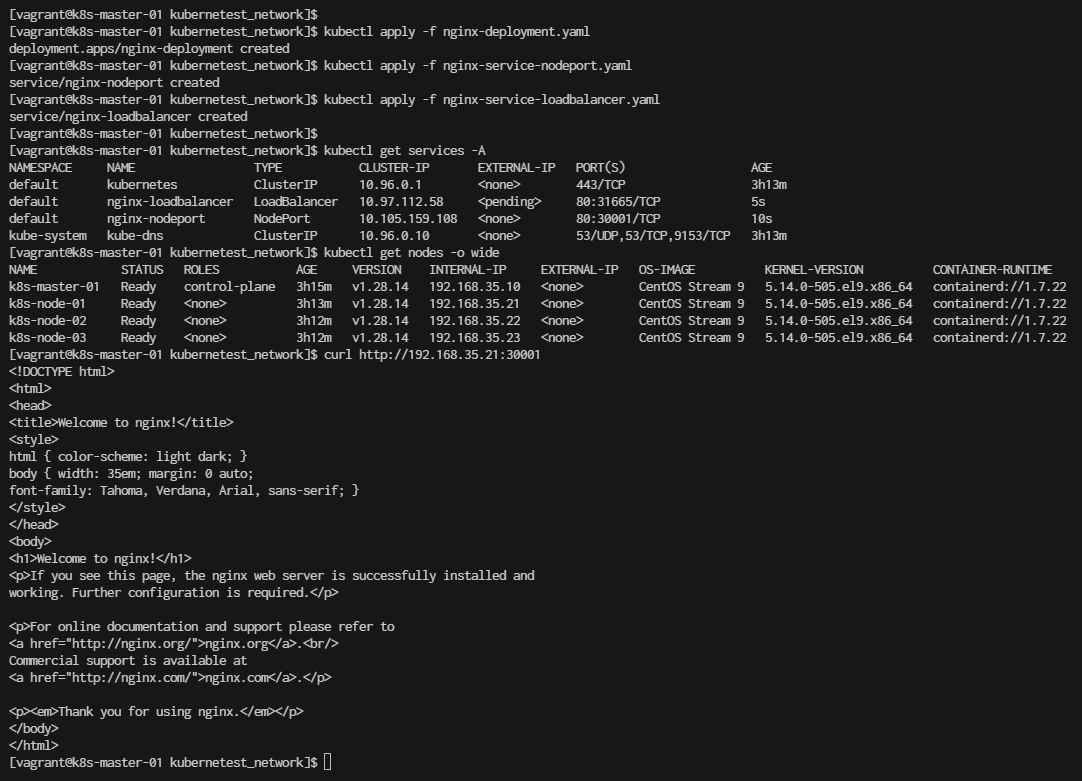
- Step3 Verification
For NodePort, use a browser or curl to access Nginx via http://<node-ip>:30001.
For LoadBalancer, once the external IP is available, access Nginx via http://<external-ip>.
Observations:
- nginx-loadbalancer: This service type is LoadBalancer, but its EXTERNAL-IP is still pending. This typically means the cluster is waiting for a cloud provider or load balancer to assign an external IP.
- nginx-nodeport: This service type is NodePort, which exposes the service on a port across all nodes. It uses port 30001 on each node, which you can use to access the service externally by hitting http://
:30001.
However, your EXTERNAL-IP is still in a pending state, which means Kubernetes is waiting for a cloud provider to assign it an external IP. This won’t work if you’re not using a supported cloud provider.
Use kubectl port-forward You can forward a port from your local machine to the service running in the cluster. This allows you to access the service locally without needing an external IP.
Run the following command:
$ kubectl port-forward svc/nginx-loadbalancer 8080:80
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 80
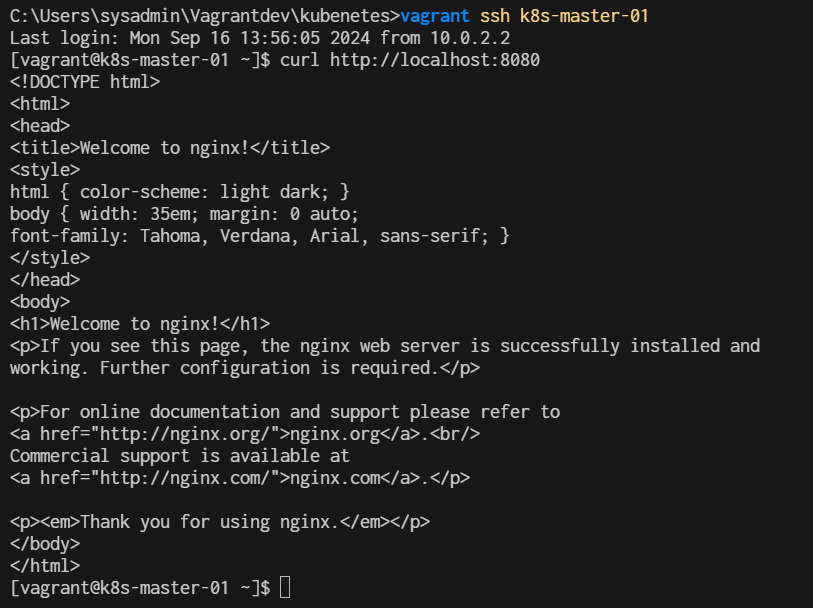
Open Second teminal and ssh to k8s-master-01
$ curl http://localhost:8080
- Clean Up Once you're done, delete the resources:
$ kubectl delete -f nginx-deployment.yaml
$ kubectl delete -f nginx-service-nodeport.yaml
$ kubectl delete -f nginx-service-loadbalancer.yaml