Jenkin menifest
https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/installing/kubernetes/
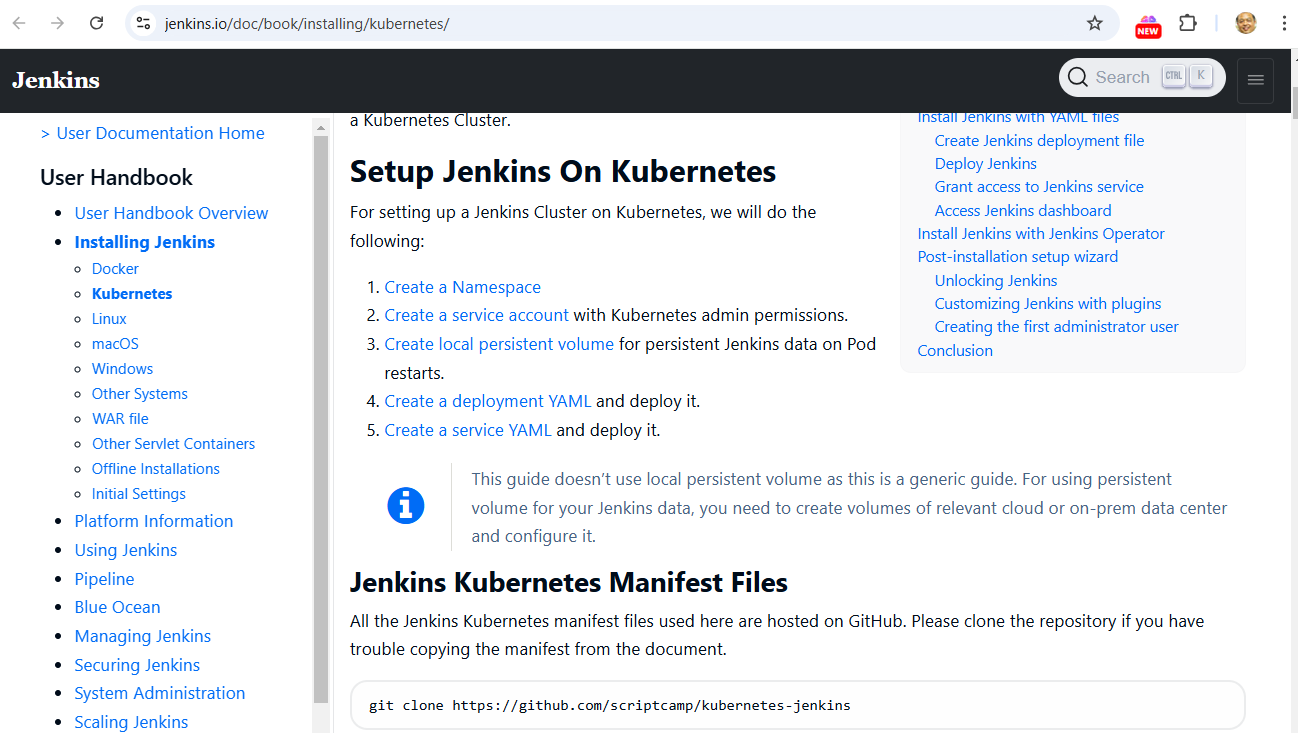
All the Jenkins Kubernetes manifest files used here are hosted on GitHub. Please clone the repository if you have trouble copying the manifest from the document.
-
Create a Namespace
-
Create a service account with Kubernetes admin permissions.
-
Create local persistent volume for persistent Jenkins data on Pod restarts.
-
Create a deployment YAML and deploy it.
-
Create a service YAML and deploy it.
git clone https://github.com/scriptcamp/kubernetes-jenkins
Kubernetes Jenkins Deployment
Let’s get started with deploying Jenkins on Kubernetes.
Step 1: Create a Namespace for Jenkins. It is good to categorize all the DevOps tools as a separate namespace from other applications.
$ kubectl create namespace devops-tools
namespace/devops-tools created
Step 2: Create a 'serviceAccount.yaml' file and copy the following admin service account manifest.
cat <<EOF | tee serviceAccount.yaml
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: jenkins-admin
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins-admin
namespace: devops-tools
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: jenkins-admin
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: jenkins-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: jenkins-admin
namespace: devops-tools
EOF
The 'serviceAccount.yaml' creates a 'jenkins-admin' clusterRole, 'jenkins-admin' ServiceAccount and binds the 'clusterRole' to the service account.
The 'jenkins-admin' cluster role has all the permissions to manage the cluster components. You can also restrict access by specifying individual resource actions.
Now create the service account using kubectl.
$ kubectl apply -f serviceAccount.yaml
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/jenkins-admin created
serviceaccount/jenkins-admin created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/jenkins-admin created
Step 3: Create 'volume.yaml' and copy the following persistent volume manifest.
cat <<EOF | tee volume.yaml
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: local-storage
provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: jenkins-pv-volume
labels:
type: local
spec:
storageClassName: local-storage
claimRef:
name: jenkins-pv-claim
namespace: devops-tools
capacity:
storage: 10Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
local:
path: /mnt
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- k8s-node-01
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: jenkins-pv-claim
namespace: devops-tools
spec:
storageClassName: local-storage
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 3Gi
EOF
Replace 'k8s-node-01' with any one of your cluster worker nodes hostname.
You can get the worker node hostname using the kubectl.
$ kubectl get nodes
Let’s create the volume using kubectl:
$ kubectl create -f volume.yaml
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/local-storage created
persistentvolume/jenkins-pv-volume created
persistentvolumeclaim/jenkins-pv-claim created
Step 4: Create a Deployment file named 'jenkins-deployment.yaml' and copy the following deployment manifest.
cat <<EOF | tee jenkins-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: devops-tools
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: jenkins-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: jenkins-server
spec:
securityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
runAsUser: 1000
serviceAccountName: jenkins-admin
containers:
- name: jenkins
image: jenkins/jenkins:lts
resources:
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "1000m"
requests:
memory: "500Mi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- name: httpport
containerPort: 8080
- name: jnlpport
containerPort: 50000
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: "/login"
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 90
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 5
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: "/login"
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 3
volumeMounts:
- name: jenkins-data
mountPath: /var/jenkins_home
volumes:
- name: jenkins-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: jenkins-pv-claim
EOF
Create the deployment using kubectl.
$ kubectl apply -f jenkins-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/jenkins created
Check deployemt status:
$ kubectl get deployments -n devops-tools
Now, you can get the deployment details using the following command.
$ kubectl describe deployments --namespace=devops-tools
create service.yaml
cat <<EOF | tee jenkins-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: jenkins-service
namespace: devops-tools
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
prometheus.io/path: /
prometheus.io/port: '8080'
spec:
selector:
app: jenkins-server
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 32000
EOF
apply service
$ kubectl apply -f jenkins-service.yaml
service/jenkins-service created
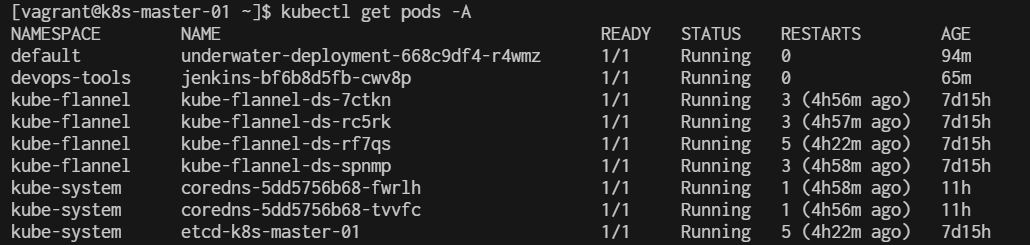
$ kubectl get pods -A
$ kubectl get svc -A
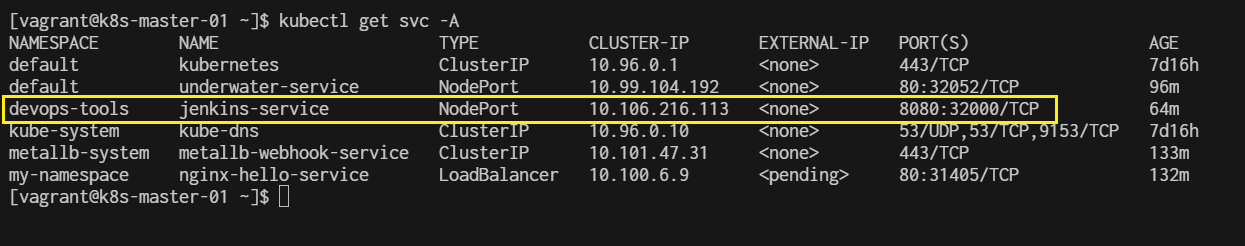
login nodeport 32000
http://192.168.35.21:32000/
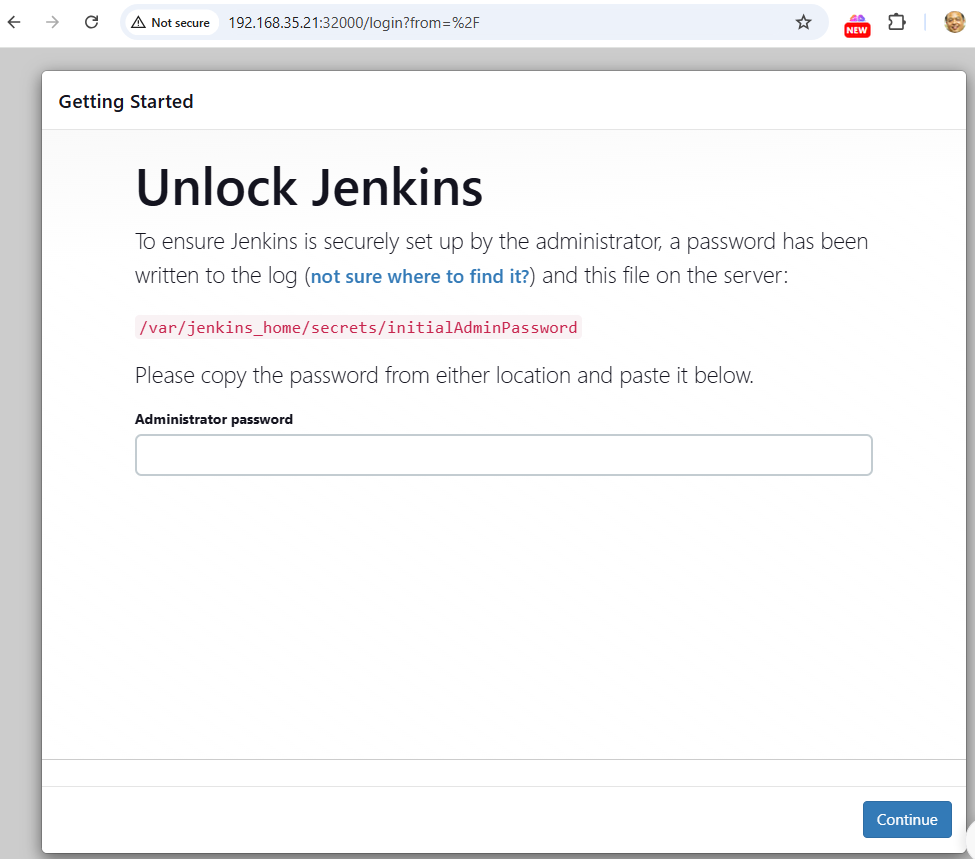
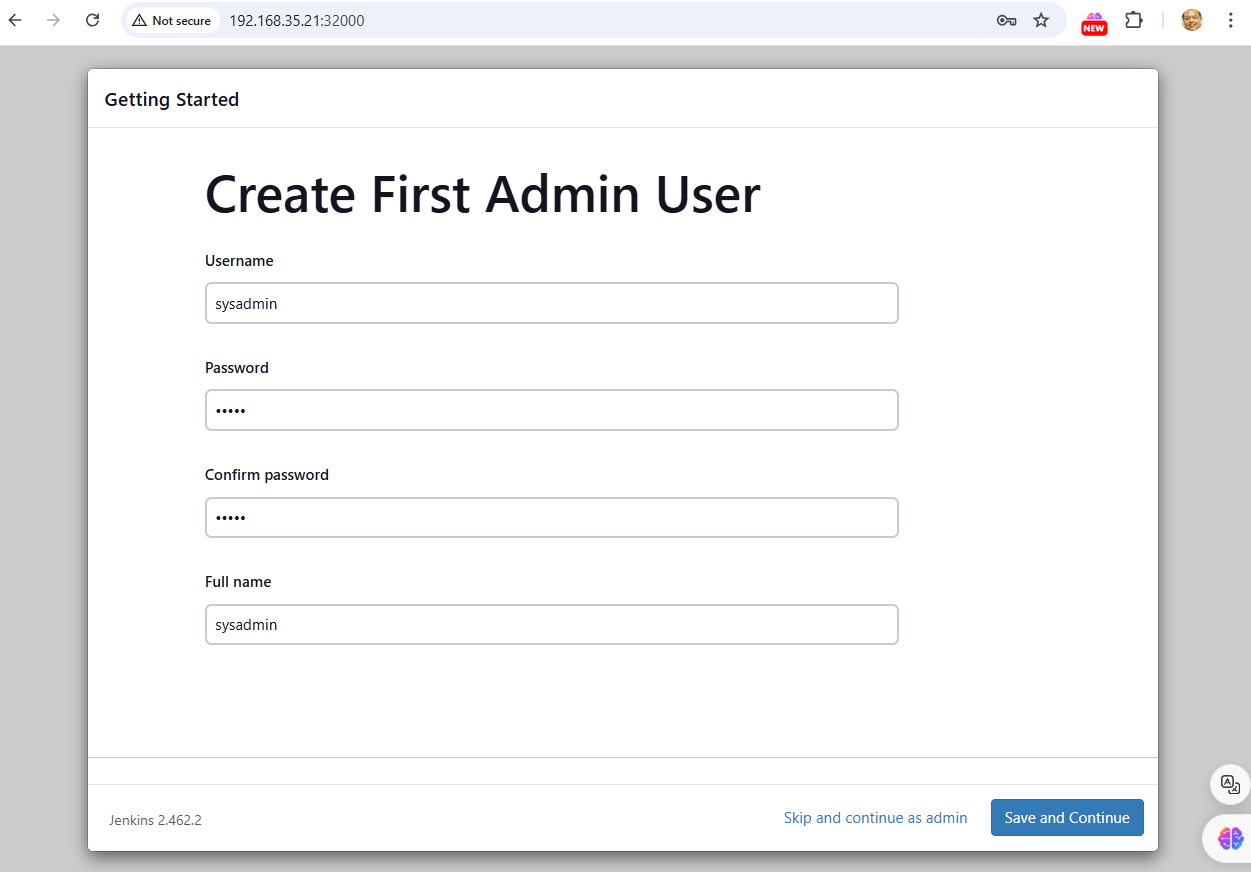
how to get /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
$ kubectl get pods -n devops-tools
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jenkins-bf6b8d5fb-cwv8p 1/1 Running 0 74m
$ kubectl exec jenkins-bf6b8d5fb-cwv8p -n devops-tools -- cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
f416325f94b54c5b91f4befc85c1baf9
[vagrant@k8s-master-01 ~]$

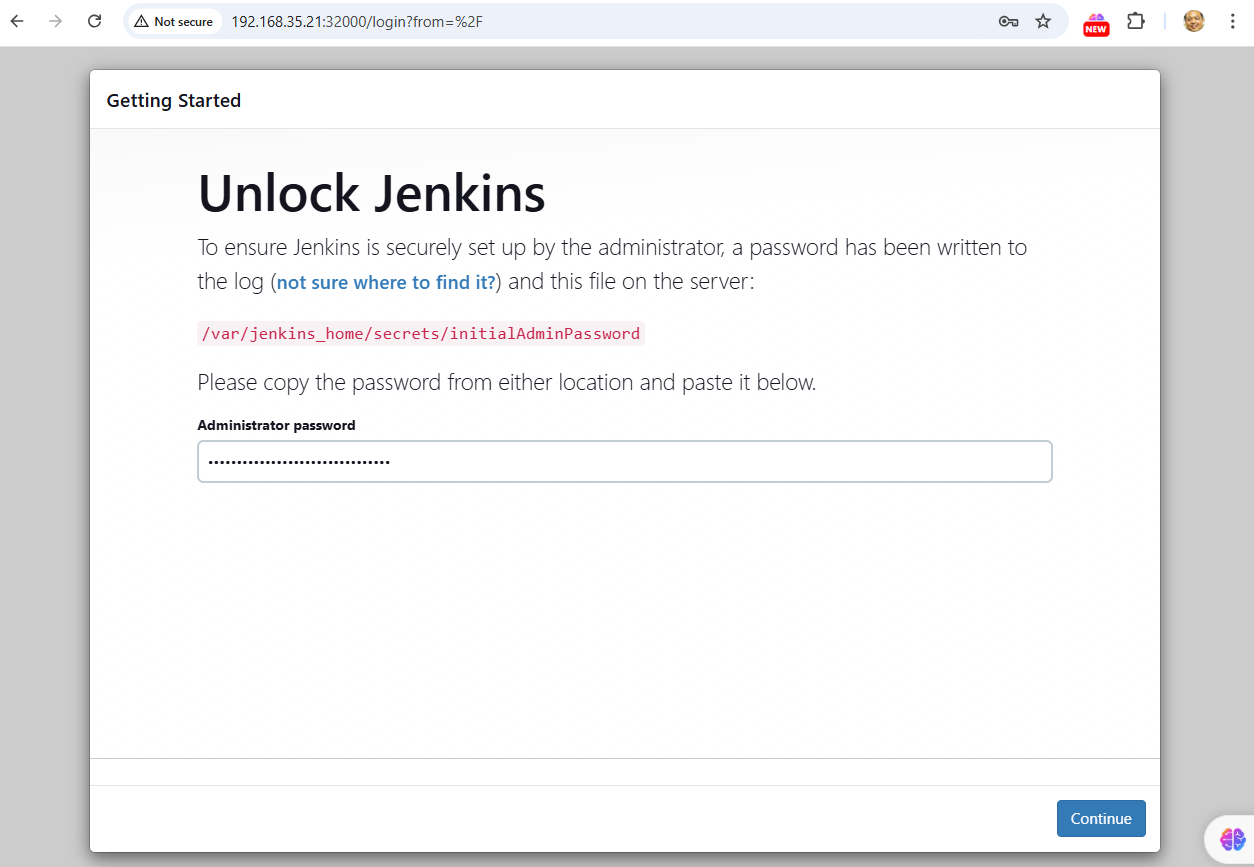
- f416325f94b54c5b91f4befc85c1baf9